
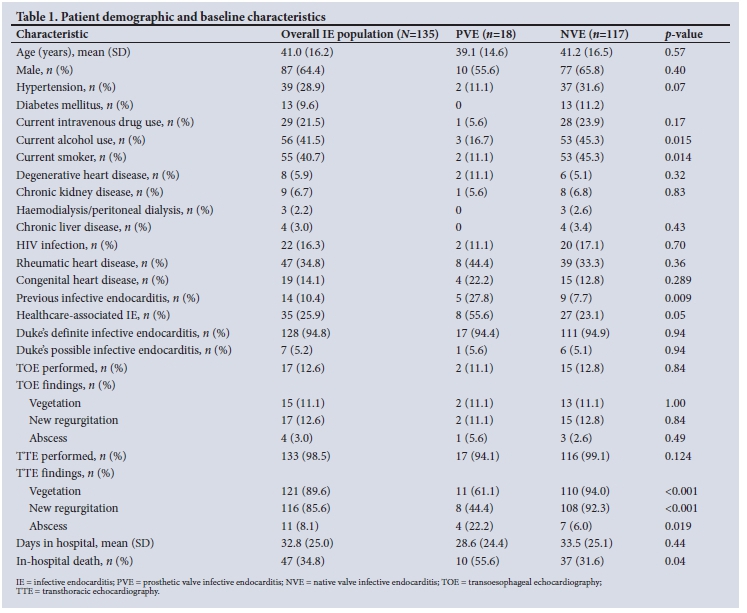
PTC has an excellent prognosis, with a cause-specific 10-year survival rate of over 90% ( Biersack & Grünwald 2005). Thyroid cancer is the fastest increasing cancer in the United States among both men and women, largely as a result of an increase in the incidence of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), which now represents approximately 90% of all new cases ( Sosa & Udelsman 2006, Jillard et al. Patients who have PTC with lymphovascular invasion should be considered higher risk, and adjuvant RAI should be more strongly considered. The presence of lymphovascular invasion among patients with PTC is independently associated with compromised survival. For patients with lymphovascular invasion, treatment with RAI was associated with reduced mortality (HR=0.43, P<0.01). After adjustment, increasing patient age (HR=1.06, P<0.01), male gender (HR=1.68, P<0.01), presence of metastatic lymph nodes (HR=1.77, P<0.01), distant metastases (HR=3.49, P<0.01), and lymphovascular invasion (HR=1.88, P<0.01) were associated with compromised survival. Unadjusted overall 5-year survival was lower for patients who had tumors with lymphovascular invasion (86.6% vs 94.5%) (log-rank P<0.01). They were also more likely to receive radioactive iodine (69.3% vs 44.9%, P<0.01). Patients with lymphovascular invasion were more likely to have larger tumors (2.8cm vs 1.5cm, P<0.01), metastatic lymph nodes (74.1% vs 32.5%, P<0.01), and distant metastases (3.0% vs 0.5%, P<0.01).

Results show that 45,415 patients met inclusion criteria 11.6% had lymphovascular invasion. A Cox proportional hazards model was utilized to identify factors associated with survival. Demographic, clinical and pathological features were evaluated for all patients.

Patients were classified into two groups based on the presence/absence of lymphovascular invasion.
The National Cancer Data Base (2010–2011) was queried for patients with PTC who underwent total thyroidectomy or lobectomy. This study sought to examine lymphovascular invasion as an independent prognostic factor for patients with PTC undergoing thyroid resection. Data are limited regarding the association between tumor lymphovascular invasion and survival for patients with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
